九坤量化开源IQuest-Coder-V1,代码大模型进入“流式”训练时代
2026第一天,由九坤投资创始团队成立的至知创新研究院(IQuest Research)开源了其最新工作 IQuest-Coder-V1 系列代码大模型,包含从 7B 到 40B 参数规模的模型,并提供标准版和 Loop 版本,并覆盖不同使用场景:
- 每个参数规模都提供Base、Instruct和Thinking三个版本
- 40B版本额外提供Loop变体,专为高效部署优化
- 所有模型均支持128K上下文长度,使用分组查询注意力(GQA)架构
| 模型 | 参数量 | 层数 | 隐藏层维度 | 注意力头数 (Q/KV) | 上下文长度 |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-7B-Instruct | 7B | 14 | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-7B-Thinking | 7B | 14 | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-14B-Instruct | 14B | 28 | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-14B-Thinking | 14B | 28 | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Instruct | 40B | 80 | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Thinking | 40B | 80 | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Loop-Instruct | 40B | 80(2 次迭代) | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
| IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Loop-Thinking | 40B | 80(2 次迭代) | 5120 | 40/8 | 128K |
IQuest 团队不仅开源了最终模型,还发布了从预训练到后训练的全阶段 checkpoint,为社区提供可追溯、可研究的“白盒”训练链条,兼顾研究、本地部署与云端应用需求。
技术报告:
https://github.com/IQuestLab/IQuest-Coder-V1/blob/main/papers/IQuest_Coder_Technical_Report.pdf
GitHub:
https://github.com/IQuestLab/IQuest-Coder-V1
模型合集:
https://modelscope.cn/collections/IQuestLab/IQuest-Coder
01研究背景
当前代码大模型在长程推理与复杂多文件代码库理解方面,仍与 Claude 4.5、GPT-5.1 等闭源领先模型存在明显差距。传统训练方法多基于静态代码快照,难以捕捉软件开发的动态演进过程,导致模型在实际工程任务中表现受限。
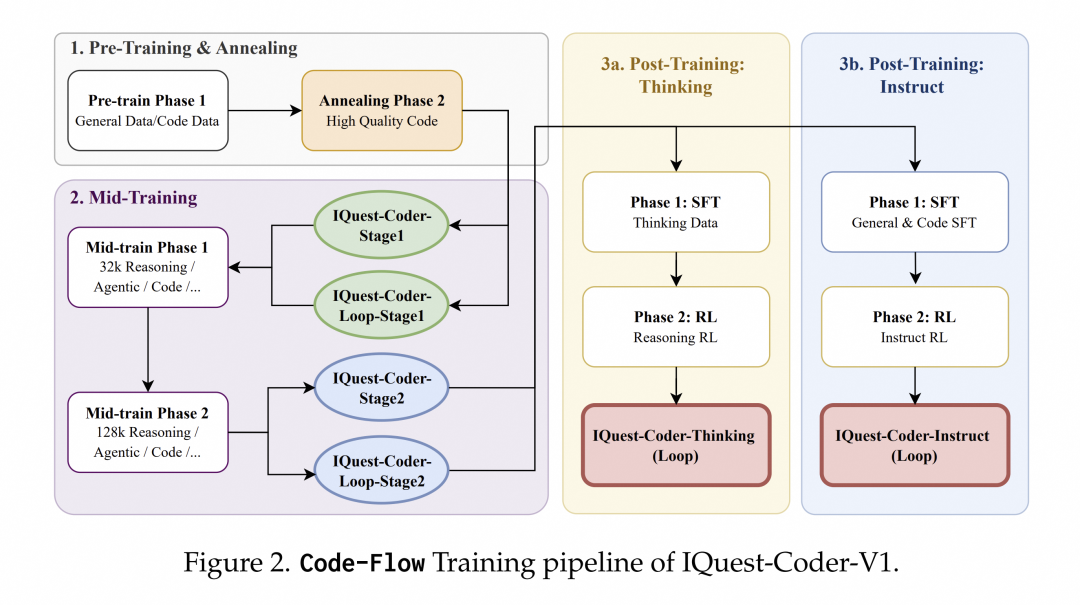
IQuest-Coder-V1 提出 Code-Flow 训练范式,通过模拟代码从提交、演化和完成的完整流程,让模型学习“代码是如何一步步写出来的”,而不仅仅是“代码长什么样”。
02研究亮点
创新的Code-Flow训练范式
IQuest-Coder-V1放弃了传统的静态代码训练模式,转而采用创新的Code-Flow多阶段训练范式。该模型通过学习代码库的历史演变和Commit记录,掌握了软件开发的动态逻辑,而非仅仅学习静态代码片段。具体训练流程分为四个核心阶段:
- 预训练与高质量退火:从通用数据和代码数据开始,经过高质量精选代码的退火阶段,确保模型基础表征为后续复杂逻辑任务做好准备
- 双阶段中间训练:在32k上下文环境中融入推理、代理轨迹和代码任务,再扩展到128k上下文进行仓库级训练
- 分叉后训练:提供两条专业化路径 - Thinking路径(使用基于推理的强化学习)和Instruct路径(优化通用辅助能力)
- 高效架构设计:Loop模型引入循环机制,在现实部署约束下优化模型容量与部署足迹之间的权衡
关键技术发现
研究团队通过系统性实验发现了几个重要规律:
- 仓库转换数据(提交流程)相比静态快照文件,能提供更优越的任务规划信号
- 在高质量代码退火后、后训练前注入32k推理和代理轨迹,可作为关键逻辑脚手架,稳定模型在分布偏移下的表现
- Thinking路径(使用RL)能触发长距离任务中自主错误恢复的涌现能力,这在标准Instruct SFT后训练路径中基本不存在
LoopCoder架构创新
LoopCoder采用循环transformer设计,其中共享参数的transformer块执行两次固定迭代:
- 第一次迭代:通过位置偏移的隐藏状态处理输入嵌入
- 第二次迭代:计算两种注意力 - 全局注意力(查询关注第一次迭代的所有键值对)和局部注意力(查询仅关注第二次迭代中前面的token)
- 通过基于查询表示的学习门控机制组合两种注意力输出,控制全局上下文细化和局部因果依赖的加权混合
这种架构使IQuest-Coder-V1可以在性能稍好的消费级硬件上运行,而不需要专业数据中心级别算力。从预训练的科学配比,到架构的递归进化,再到Agent能力的工具化和自我合成,形成了一个完美的闭环。
03模型评测表现
全面领先的基准测试结果
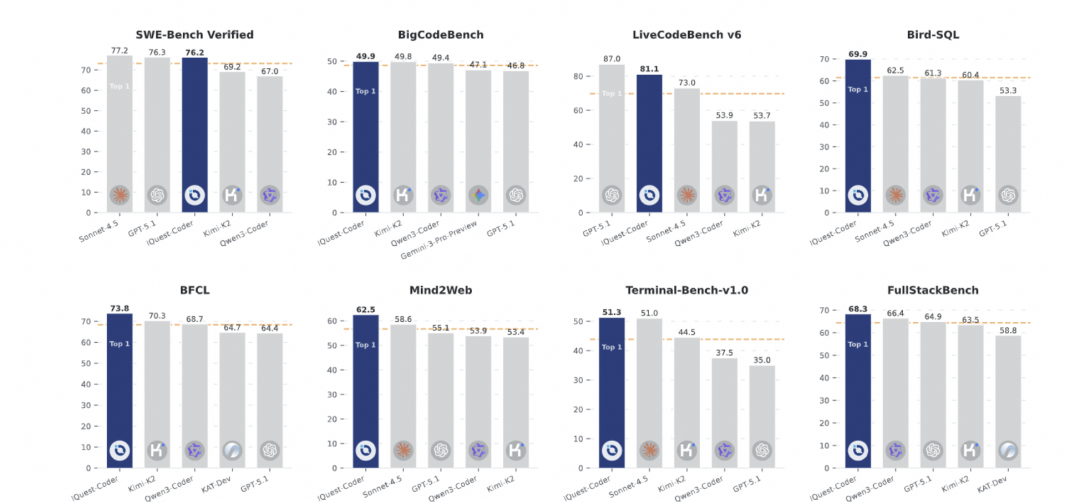
IQuest-Coder-V1在多项权威基准测试中展现出色性能:
- SWE-Bench Verified:达到76.2分,在相同参数量下,领先其他开源模型
- BigCodeBench:获得49.9分,超越同类开源模型
- LiveCodeBench v6:IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Loop-Thinking模型达到87.0分
- Bird-SQL:得分73.8,显著优于其他开源方案
- 终端任务:在Terminal-Bench-v1.0上达到68.3分,展示强大的命令行工具使用能力
- 全栈开发:在FullStackBench上表现优异,证明其处理复杂工程任务的能力
特定任务优势
在代码效率评估中,IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Instruct在Mercury基准上达到83.6分(Pass@1)和95.3分(Beyond@1),表明其不仅能生成正确代码,还能产生运行时间高效的结果;在Text-to-SQL任务中,该模型在Bird基准上达到70.5分,在Spider基准上达到92.2分,显示出卓越的语义解析和查询生成能力。
在代理编码任务中,IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Loop-Instruct在SWE-Bench Verified上达到76.2分,在Terminal-Bench上达到51.3分,证明其在真实软件工程场景中的实用价值;在通用工具使用任务中,该模型在Mind2Web和BFCL V3基准上也表现突出,分别达到62.5分和73.9分。
04模型实践实践
使用 Transformers 推理
建议使用 transformers>=4.52.4,以IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Instruct为例
from modelscope import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "IQuestLab/IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Instruct"
# Load the tokenizer and model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# Prepare the input
prompt = "Write a Python function to calculate the Fibonacci sequence using dynamic programming."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# Generate response
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=8192
)
generated_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):]
response = tokenizer.decode(generatd_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(response)
使用 vLLM 部署推理
VLLM_USE_MODELSCOPE=true vllm serve IQuest/IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Instruct --tensor-parallel-size 8对于支持推理的 Thinking 模型:
VLLM_USE_MODELSCOPE=true vllm serve IQuest/IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Thinking --reasoning-parser qwen3 --tensor-parallel-size 8
使用 ms-swift 微调
ms-swift支持了对 IQuest-Coder 的微调。ms-swift是魔搭社区官方提供的大模型与多模态大模型训练部署框架。ms-swift开源地址:https://github.com/modelscope/ms-swift
在开始微调之前,请确保您的环境已准备妥当。
pip install "transformers==4.52.4"
# pip install git+https://github.com/modelscope/ms-swift.git
git clone https://github.com/modelscope/ms-swift.git
cd ms-swift
pip install -e .自定义数据集格式如下,并在命令行中设置`--dataset train.jsonl --val_dataset val.jsonl`,验证集为可选。
{"messages": [{"role": "system", "content": "<system>"}, {"role": "user", "content": "<query1>"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "<response1>"}, {"role": "user", "content": "<query2>"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "<response2>"}]}以下提供可直接运行的微调脚本,显存占用2 * 50GiB:
PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF='expandable_segments:True' \
NPROC_PER_NODE=2 \
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 \
swift sft \
--model IQuestLab/IQuest-Coder-V1-40B-Instruct \
--dataset 'AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-zh#500' \
'AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-en#500' \
'swift/self-cognition#500' \
--load_from_cache_file true \
--split_dataset_ratio 0.01 \
--train_type lora \
--torch_dtype bfloat16 \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
--lora_rank 8 \
--lora_alpha 32 \
--target_modules all-linear \
--gradient_checkpointing true \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 1 \
--eval_steps 100 \
--save_steps 100 \
--save_total_limit 2 \
--logging_steps 5 \
--max_length 2048 \
--output_dir output \
--warmup_ratio 0.05 \
--dataset_num_proc 4 \
--model_author swift \
--model_name swift-robot \
--deepspeed zero3 \
--dataloader_num_workers 4训练结束后,我们使用以下脚本进行推理:
PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF='expandable_segments:True' \
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 \
swift infer \
--adapters output/vx-xxx/checkpoint-xxx \
--stream true \
--max_new_tokens 2048推送模型到ModelScope:
swift export \
--adapters output/vx-xxx/checkpoint-xxx \
--push_to_hub true \
--hub_model_id '<your-model-id>' \
--hub_token '<your-sdk-token>'模型合集:https://modelscope.cn/collections/IQuestLab/IQuest-Coder
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献909条内容
已为社区贡献909条内容










所有评论(0)